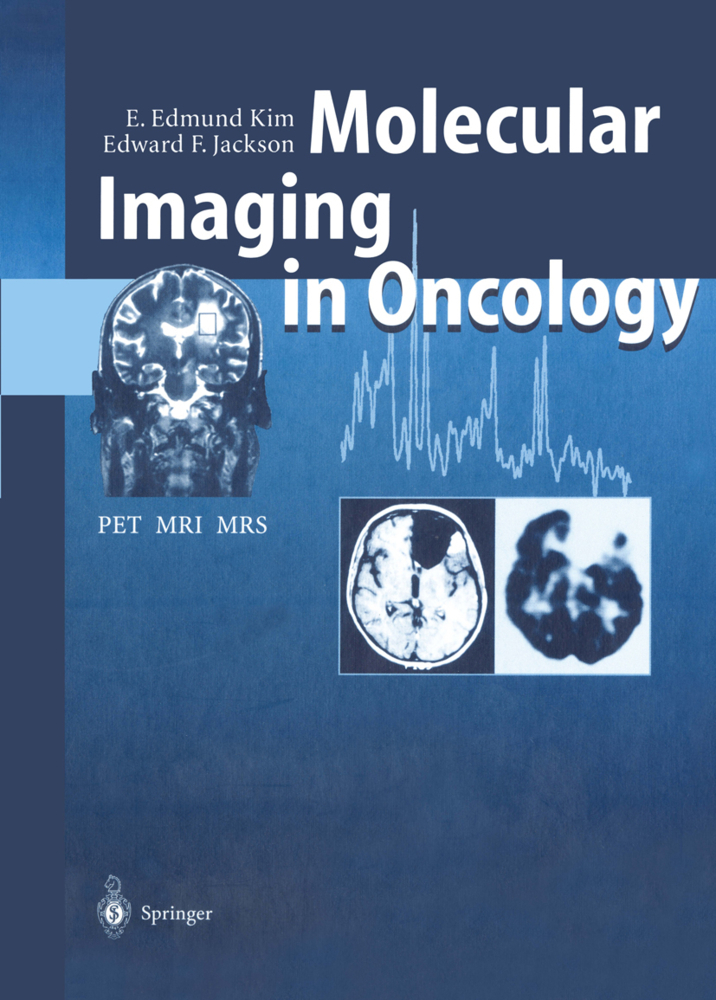
Cerebral Ischemia
Cerebral Ischemia
Despite a worldwide reduction in its incidence, stroke remains one of the most common diseases generally and the most important cause of premature and persistent disability in the industrialized countries. The most frequent cause of stroke is a localized disturbance of cerebral circulation, i.e., cerebral ischemia. Less common are spon taneous intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhages and sinus ve nous thromboses. The introduction of new diagnostic procedures such as cranial computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, digi tal subtraction radiologic techniques, and various ultrasound tech niques has led to impressive advances in the diagnosis of stroke. Through the planned application of these techniques, it is even possible to identify the pathogenetic mechanisms underlying focal cerebral ischemia in humans. However, these diagnostic advances have made the gap between diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic implications even greater than before. This fact can be easily explained. In the past, therapeutic studies had to be based on the symptoms and temporal aspects of stroke; it was impossible for early investigations to consider the various pathogeneses of cerebral ischemia. Inevitably, stroke patients were treated as suffering from a uniform disease.
1.2 Intracranial Anatomy
1.3 Collaterals and Anastomoses
1.4 Arterial Anatomy and Infarct Types
References
2 Pathophysiology of Cerebral Ischemia
2.1 Introduction
2.2 General Aspects of Brain Cell Metabolism
2.3 Regulation of Cerebral Circulation
2.4 Cerebral Ischemia
2.5 Ischemic Cerebral Edema
References
3 Epidemiology and Classification of Strokes
3.1 Epidemiology
3.2 Definitions and Classification of Strokes
References
4 Clinical Syndromes, Pathogenesis, and Differential Diagnosis
4.1 Symptoms and Syndromes-Temporal and Topical Aspects
4.2 Pathogenetic Aspects
4.3 Special Types
4.4 Differential Diagnosis
4.5 Thrombosis of Cerebral Venous Sinuses
References
5 Diagnosis
5.1 History and Clinical Findings
5.2 Ultrasound Diagnosis
5.3 Computer-Assisted Imaging Techniques
5.4 Electrophysiologic Investigations
5.5 Cerebral Angiography
References
6 Treatment and Prophylaxis
6.1 General Treatment
6.2 Special Treatment in the Acute Phase
6.3 Prophylaxis of Cerebral Ischemia
6.4 Rehabilitation in Cerebrovascular Diseases
References.
1 Applied Anatomy of the Cerebral Arteries
1.1 Extracranial Anatomy1.2 Intracranial Anatomy
1.3 Collaterals and Anastomoses
1.4 Arterial Anatomy and Infarct Types
References
2 Pathophysiology of Cerebral Ischemia
2.1 Introduction
2.2 General Aspects of Brain Cell Metabolism
2.3 Regulation of Cerebral Circulation
2.4 Cerebral Ischemia
2.5 Ischemic Cerebral Edema
References
3 Epidemiology and Classification of Strokes
3.1 Epidemiology
3.2 Definitions and Classification of Strokes
References
4 Clinical Syndromes, Pathogenesis, and Differential Diagnosis
4.1 Symptoms and Syndromes-Temporal and Topical Aspects
4.2 Pathogenetic Aspects
4.3 Special Types
4.4 Differential Diagnosis
4.5 Thrombosis of Cerebral Venous Sinuses
References
5 Diagnosis
5.1 History and Clinical Findings
5.2 Ultrasound Diagnosis
5.3 Computer-Assisted Imaging Techniques
5.4 Electrophysiologic Investigations
5.5 Cerebral Angiography
References
6 Treatment and Prophylaxis
6.1 General Treatment
6.2 Special Treatment in the Acute Phase
6.3 Prophylaxis of Cerebral Ischemia
6.4 Rehabilitation in Cerebrovascular Diseases
References.
Hacke, Werner
Hennerici, Michael
Gelmers, Herman J.
| ISBN | 978-3-642-75550-7 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783642755507 |
| Medientyp | Buch |
| Copyrightjahr | 2012 |
| Verlag | Springer, Berlin |
| Umfang | XI, 238 Seiten |
| Abbildungen | XI, 238 p. 73 illus. |
| Sprache | Englisch |