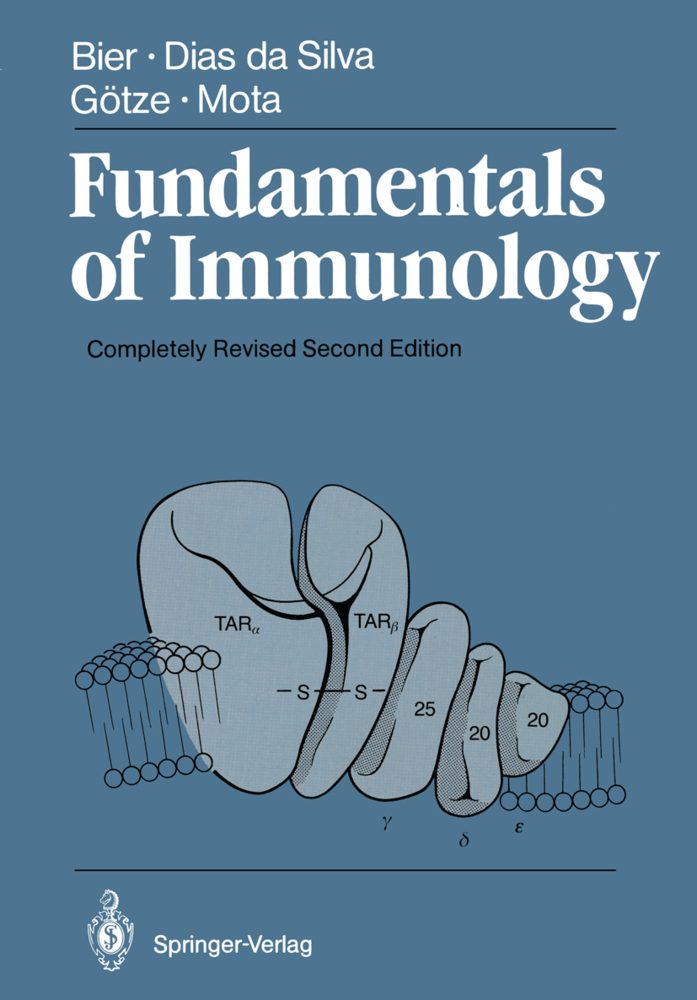
Complement
Complement
Activation of the complement system gives rise to a number of molecular species which can interact with host-derived cells and regulate their function. This interaction is mediated through distinct cell surface complement receptors, and receptor engagement produces biologic responses which can either modulate host defense reactions or enhance inflammation. Although the first complement receptor was recognized more than 30 years ago [80J, detailed biochemical information concerning the receptors has only recently become available. Currently, eight distinct complement receptors are recognized. Five receptors (CRl, CR2, CR3, C3a receptor, and C3e receptor) react with various regions on C3 while the other receptors display specificity for Clq, C5a, or Factor H. This chapter focusses on the chemistry of the various ligands and receptors and discusses the biologic activities which arise as a result of receptor-ligand interaction. II. CIQ Receptor A. The Ligand Clq is the recognition molecule of the classical complement pathway [reviewed in 20, 130]. In serum, it is part of a calcium-dependent penta molecular complex containing one molecule ofClq and two molecules each of the pro enzymes Clr and CIs. During classical pathway activation, the macromolecular complex becomes associated with the activator through the Clq subcomponent. Bound Clq undergoes a conformational change and induces the proteolytic autoactivation of Clr which in turn effects the proteolytic activation of CIs. This process is controlled by the Cl inhibitor (ClINH) which binds irreversibly to activated Clr and CIs, and inhibits their enzymatic activities.
Structure and Expression of the C3 Gene
Molecular Genetics of the Major Histocompatibility Linked Complement Genes
The ?-Cys-?-Glu Thiolester Bond in Human C3 and C4, and ?2-Macroglobulin
Structure and Function of the Anaphylatoxins
The Human C3b Receptor
The Chemistry and Biology of Complement Receptors
Molecular Mechanisms
Initiation of Complement Activation
The First Component of Human Complement (Cl): Activation and Control
The Alternative Pathway of Complement
The Role of Antibody in the Activation of the Alternative Complement Pathway
The Membrane Attack Complex
Biologic Aspects
Synthesis of Complement by Macrophages and Modulation of Their Functions Through Complement Activation
Regulation of Immune Response by Components of the Complement Cascade and Their Activated Fragments
Complement, Viruses, and Virus-Infected Cells
The Role of Complement in Host Resistance to Bacteria
Relationships Among the Complement, Kinin, Coagulation, and Fibrinolytic Systems
Pathologic Aspects
Inherited Deficiencies of Complement Proteins in Man
The Role of Complement in Experimental Disease Models
The Role of Complement in Immune Clearance of Blood Cells
Methods to Detect and Quantitate Complement Activation
Addendum to: Synthesis of Complement by Macrophages and Modulation of Their Functions Through Complement Activation.
and Overview
Basic AspectsStructure and Expression of the C3 Gene
Molecular Genetics of the Major Histocompatibility Linked Complement Genes
The ?-Cys-?-Glu Thiolester Bond in Human C3 and C4, and ?2-Macroglobulin
Structure and Function of the Anaphylatoxins
The Human C3b Receptor
The Chemistry and Biology of Complement Receptors
Molecular Mechanisms
Initiation of Complement Activation
The First Component of Human Complement (Cl): Activation and Control
The Alternative Pathway of Complement
The Role of Antibody in the Activation of the Alternative Complement Pathway
The Membrane Attack Complex
Biologic Aspects
Synthesis of Complement by Macrophages and Modulation of Their Functions Through Complement Activation
Regulation of Immune Response by Components of the Complement Cascade and Their Activated Fragments
Complement, Viruses, and Virus-Infected Cells
The Role of Complement in Host Resistance to Bacteria
Relationships Among the Complement, Kinin, Coagulation, and Fibrinolytic Systems
Pathologic Aspects
Inherited Deficiencies of Complement Proteins in Man
The Role of Complement in Experimental Disease Models
The Role of Complement in Immune Clearance of Blood Cells
Methods to Detect and Quantitate Complement Activation
Addendum to: Synthesis of Complement by Macrophages and Modulation of Their Functions Through Complement Activation.
Müller-Eberhard, H. J.
Miescher, P. A.
| ISBN | 978-3-540-15075-6 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783540150756 |
| Medientyp | Buch |
| Copyrightjahr | 1985 |
| Verlag | Springer, Berlin |
| Umfang | VI, 474 Seiten |
| Abbildungen | VI, 474 p. 35 illus. |
| Sprache | Englisch |