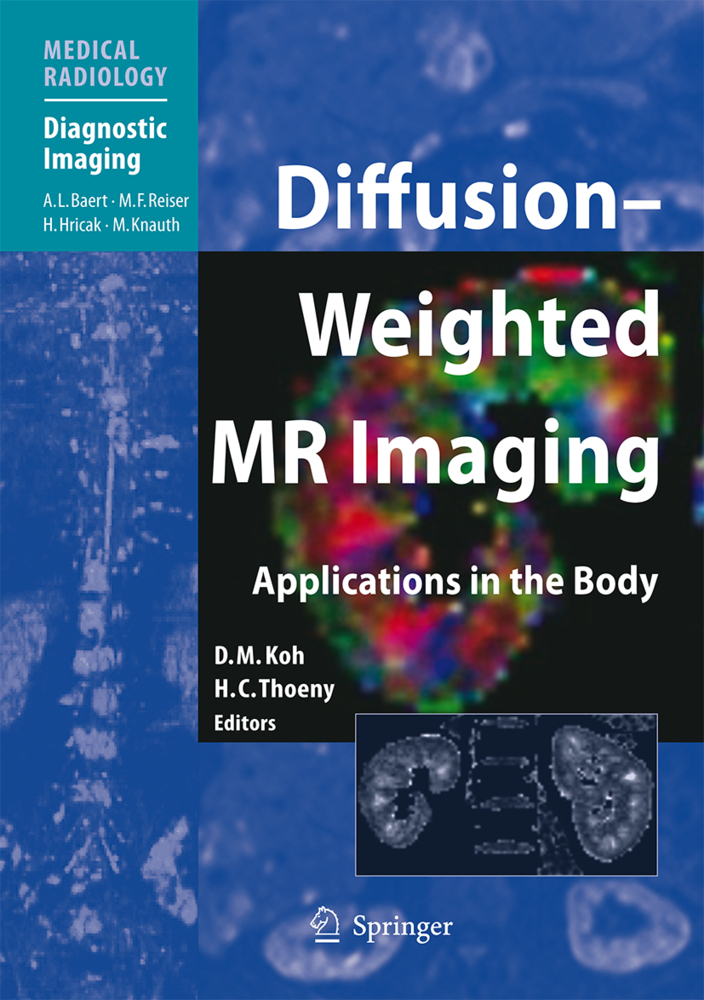
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
Applications in the Body
The clinical applications of diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DW-MRI) in the body are rapidly evolving. This volume highlights state-of-the-art techniques for performing DW-MRI measurement in the body and addresses important practical issues. Key points are highlighted that will help radiologists and technologists to acquire high-quality images for disease assessment and to adapt the technique to their own clinical practice or research. The major clinical applications of DW-MRI in the body, both oncological and non-oncological, are extensively illustrated, providing readers with a broad insight into the growing uses of the technique. The final section addresses future developments, considering the potential importance of the technique in relation to drug development and the ways in which DW-MRI might be combined with other functional imaging techniques to further improve disease assessment.
1.6;Part I: Principles and Background;9 1.6.1;Chapter 1;10 1.6.1.1;Principles of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DW-MRI) as Applied to Body Imaging;10 1.6.1.1.1;1.1 Introduction;10 1.6.1.1.2;1.2 Basic Diffusion Concepts;11 1.6.1.1.3;1.3 Magnetic Resonance Measurement of Diffusion;12 1.6.1.1.4;1.4 Anisotropic Diffusion;13 1.6.1.1.5;1.5 Diffusion Measurements In Vivo;14 1.6.1.1.6;1.6 Effect of Perfusion and Low b-Valueon ADC Estimation;15 1.6.1.1.7;1.7 Effect of SNR and High b-Value on ADC Estimation;17 1.6.1.1.8;1.8 Multi-Exponential Diffusion in Tissues;19 1.6.1.1.9;1.9 Conclusion;22 1.6.1.1.10;References;22 1.6.2;Chapter 2;25 1.6.2.1;Techniques and Optimization;25 1.6.2.1.1;2.1 Introduction;25 1.6.2.1.2;2.2 Factors that Aff ect Image Quality Using EPI DW-MRI Acquisition;26 1.6.2.1.2.1;2.2.1 Image Signal-to-Noise (SNR);26 1.6.2.1.2.2;2.2.2 Image Artefacts;26 1.6.2.1.3;2.3 Bulk Diffusion Phantoms;27 1.6.2.1.4;2.4 Optimizing Image Quality on Volunteer or Patient Studies;30 1.6.2.1.4.1;2.4.1 Fat Suppression;31 1.6.2.1.4.2;2.4.2 Single-Shot Acquisition vs. Multiple Signals Averaging;32 1.6.2.1.5;2.5 Optimization Strategies for the Selection of b-Values;33 1.6.2.1.5.1;2.5.1 Quantitative Data;33 1.6.2.1.5.2;2.5.2 Qualitative Data;34 1.6.2.1.6;2.6 Summary of Technique Optimization for DW-MRI in the Body;36 1.6.2.1.7;References;37 1.6.3;Chapter 3;39 1.6.3.1;Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses: Image Evaluation and Interpretation;39 1.6.3.1.1;3.1 Introduction;39 1.6.3.1.2;3.2 Qualitative Assessment of DW-MR Images;40 1.6.3.1.2.1;3.2.1 DW-MR Images Acquired Using Different b-Values;40 1.6.3.1.2.1.1;3.2.1.1 T2 Shine-Through;41 1.6.3.1.2.1.2;3.2.1.2 Diffusion Anisotropy;42 1.6.3.1.2.2;3.2.2 ADC Maps;43 1.6.3.1.2.3;3.2.3 Principles of Image Interpretation Using DW-MRI and ADC Maps;45 1.6.3.1.3;3.3 Quantitative ADC Evaluation;47 1.6.3.1.3.1;3.3.1 Quantitative ADC Evaluation by Regions of Interests;47 1.6.3.1.3.1.1;3.3.1.1 Summary Statistics;47 1.6.3.1.3.1.2;3.3.1.2 Voxelwise Analysis;47 1.6.3.1.3.2;3.3.2 Software for ADC Calculation;48 1.6.3.1.3.3;3.3.3Applying Quantitative ADCValues for Disease Characterization;48 1.6.3.1.3.4;3.3.4 Measurement Reproducibility;50 1.6.3.1.4;3.4 Image Display;50 1.6.3.1.4.1;3.4.1 Display of the b-Value DW-MR Images;50 1.6.3.1.4.2;3.4.2 Image Fusion;50 1.6.3.1.4.3;3.4.3 Diffusion-weighted Whole-body Imaging with Background Body Signal Suppression (DWIBS);52 1.6.3.1.5;3.5 Conclusions;52 1.6.3.1.6;References;52 1.7;Part II: Non-Oncological Applications in the Body;54 1.7.1;Chapter 4;55 1.7.1.1;MR Neurography: Imaging of the Peripheral Nerves;55 1.7.1.1.1;4.1 Introduction;55 1.7.1.1.2;4.2 Concepts of MR Neurography;56 1.7.1.1.2.1;4.2.1 Conventional MR Neurography;56 1.7.1.1.2.2;4.2.2 Visualization of Nerves Using DW-MRI;57 1.7.1.1.2.3;4.2.3 Difference Between Diffusion-Weighted MR Neurography and Diffusion Tensor Imaging/Tractography;58 1.7.1.1.2.4;4.2.4 DWIBS for Diffusion-Weighted MR Neurography;58 1.7.1.1.3;4.3 Technical Aspects;59 1.7.1.1.3.1;4.3.1 Basic Parameter Settings;59 1.7.1.1.3.2;4.3.2 Fat Suppression;59 1.7.1.1.3.3;4.3.3 Post-Processing by Maximum Intensity Projection;60 1.7.1.1.3.4;4.3.4 Unidirectionally Encoded Diffusion-Weighted MR Neurography;61 1.7.1.1.4;4.4 Normal Anatomy;62 1.7.1.1.4.1;4.4.1 General Image-Based Peripheral Nerve Anatomy;62 1.7.1.1.4.2;4.4.2 Brachial Plexus;63 1.7.1.1.4.3;4.4.3 Lumbosacral Plexus;64 1.7.1.1.5;4.5 Clinical Applications of Diffusion-Weighted MR Neurography;64 1.7.1.1.5.1;4.5.1 Neurogenic Tumours;64 1.7.1.1.5.2;4.5.2 Trauma;66 1.7.1.1.5.3;4.5.3 Mechanical Nerve Compression;66 1.7.1.1.5.4;4.5.4 Inflammatory Processes;68 1.7.1.1.6;References;71 1.7.2;Chapter 5;72 1.7.2.1;Evaluation of Organ Function;72 1.7.2.1.1;5.1 Introduction;72 1.7.2.1.2;5.2 Effect of b-Values;73 1.7.2.1.3;5.3 Salivary Glands;74 1.7.2.1.3.1;5.3.1 Introduction;74 1.7.2.1.3.2;5.3.2 Imaging at Rest;74 1.7.2.1.3.3;5.3.3 Imaging During and After Stimulation;74 1.7.2.1.3.4;5.3.4 Comparison with Salivary
| ISBN | 9783540785767 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783540785767 |
| Medientyp | E-Book - PDF |
| Auflage | 2. Aufl. |
| Copyrightjahr | 2010 |
| Verlag | Springer-Verlag |
| Umfang | 299 Seiten |
| Kopierschutz | Digitales Wasserzeichen |