Process Integration and Intensification
Saving Energy, Water and Resources
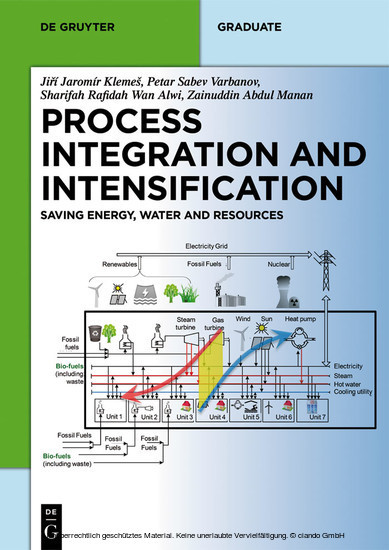
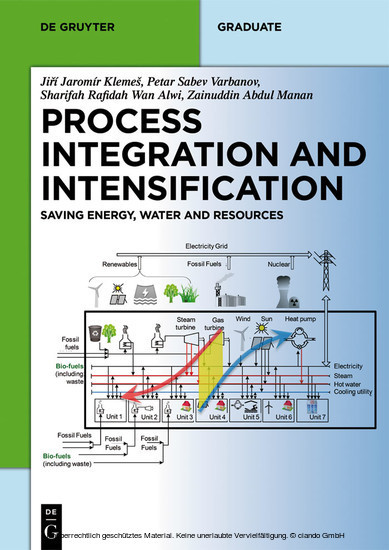
Process Integration and Intensification (PII) is one of the most timely topics in chemical and process engineering leading to energy efficient, substantially smaller, cleaner, safer and optimized processes. The book covers optimization fundamentals and industrial applications. It is an authoritative overview meant to help graduate students as well as professionals to effectively apply PII in plant design and operation.
Jirí J. Kleme?and Petar S. Varbanov, University of Pannonia, Hungary;Sharifah R.W.Alwi and Zainuddin A.Manan, UTM, Johor, Malaysia.
1;Preface;5 2;Acronyms, abbreviations and symbols;11 3;1 Process Integration and Intensification: an introduction;15 3.1;1.1 Process Intensification;15 3.2;1.2 Process Systems Engineering and Process Integration;17 3.3;1.3 Contributions to PIs and PI to energy and water saving;18 3.4;1.4 What is Process Integration?;18 3.5;1.5 A brief history of the development of Process Integration;19 3.6;1.6 The aim and scope of this textbook;22 3.7;References;23 4;2 Setting energy targets and Heat Integration;27 4.1;2.1 Introduction;27 4.1.1;2.1.1 Initial development of Heat Integration;28 4.1.2;2.1.2 Pinch Technology and targeting Heat Recovery: the thermodynamic roots;28 4.1.3;2.1.3 Supertargeting: full-fledged HEN targeting;29 4.1.4;2.1.4 Modifying the Pinch Idea for HEN retrofit;30 4.1.5;2.1.5 Benefits of Process Integration;30 4.2;2.2 Pinch Analysis for maximising energy efficiency;31 4.2.1;2.2.1 Introduction to Heat Exchange and Heat Recovery;31 4.2.2;2.2.2 Basic principles;33 4.2.3;2.2.3 Basic Pinch Technology;42 4.3;2.3 Summary;77 4.4;References;78 5;3 Synthesis of Heat Exchanger Networks;81 5.1;3.1 Introduction;81 5.2;3.2 HEN synthesis;81 5.2.1;3.2.1 The Pinch Design Method;82 5.2.2;3.2.2 Methods using mathematical programming;103 5.3;3.3 Grassroots and retrofits, impact of economic criteria;107 5.3.1;3.3.1 Network optimisation;107 5.3.2;3.3.2 The Network Pinch;108 5.4;3.4 Summary;110 5.5;References;110 6;4 Total Site Integration;113 6.1;4.1 Introduction;113 6.2;4.2 What is a Total Site and what are the benefits?;114 6.2.1;4.2.1 Total Site definition;115 6.2.2;4.2.2 Total Site Analysis interfaces;116 6.3;4.3 HI extension for Total Sites: data extraction for Total Sites;117 6.3.1;4.3.1 The algorithm;117 6.3.2;4.3.2 Step-by-step guidance;119 6.3.3;4.3.3 Working session;123 6.4;4.4 Total Site Profiles and Total Site Composite Curves;124 6.5;4.5 Site Utility Grand Composite Curve (SUGCC);132 6.6;4.6 Combined Heat and Power Generation (CHP, Cogeneration) targeting;134 6.6.1;4.6.1 A simple cogeneration model;135 6.6.2;4.6.2 Targeting CHP using the SUGCC;136 6.6.3;4.6.3 Choice of optimal steam pressure levels;138 6.7;4.7 Advanced Total Site developments;140 6.7.1;4.7.1 Introduction of process-specific minimum allowed temperature differences;140 6.7.2;4.7.2 Numerical tools for Total Site Heat Integration;141 6.7.3;4.7.3 Power Integration;142 6.8;4.8 Summary;147 6.9;References;148 7;5 Introduction to Water Pinch Analysis;151 7.1;5.1 Water management and minimisation;151 7.2;5.2 History and definition of Water Pinch Analysis;152 7.3;5.3 Applications of Water Pinch Analysis;153 7.4;5.4 Water Pinch Analysis steps;154 7.5;5.5 Analysis of water networks and data extraction;155 7.5.1;5.5.1 Analysis of water networks;155 7.5.2;5.5.2 Data extraction;157 7.5.3;5.5.3 Example;158 7.6;References;162 8;6 Setting the maximum water recovery targets;165 8.1;6.1 Introduction;165 8.2;6.2 Maximum water recovery target for single pure freshwater;169 8.2.1;6.2.1 Water Cascade Analysis technique;169 8.2.2;6.2.2 Source/Sink Composite Curves (SSCC);172 8.2.3;6.2.3 Significance of the Pinch region;173 8.3;6.3 Maximum water recovery target for a single impure freshwater source;174 8.3.1;6.3.1 Pinched problems;174 8.3.2;6.3.2 Threshold problems;180 8.4;6.4 Maximum water recovery targets for multiple freshwater sources;182 8.5;6.5 Working session;184 8.6;6.6 Solution;184 8.7;References;188 9;7 Water network design/retrofit;191 9.1;7.1 Introduction;191 9.2;7.2 Source/Sink Mapping Diagram (SSMD);191 9.3;7.3 Source and Sink Allocation Curves (SSAC);193 9.3.1;7.3.1 Example of network design using SSCC for utility purity superior to all other streams;197 9.3.2;7.3.2 Freshwater purity not superior to all other streams;200 9.3.3;7.3.3 Simplification of a water network or constructing other network possibilities;203 9.4;7.4 Working session;206 9.5;7.5 Solution;207 9.6;7.6 Water MATRIX software;209 9.7;References;210 10;8 Design of Cost-Effective Minimum Water Network (CEMWN)
Kleme, Jirí Jaromír
Varbanov, Petar Saebev
Alwi, Sharifah Rafidah Wan
Manan, Zainuddin Abdul
| ISBN | 9783110368246 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783110368246 |
| Medientyp | E-Book - ePUB |
| Copyrightjahr | 2014 |
| Verlag | Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co.KG |
| Umfang | 265 Seiten |
| Sprache | Englisch |
| Kopierschutz | Digitales Wasserzeichen |