Protein Modules in Signal Transduction
Protein Modules in Signal Transduction
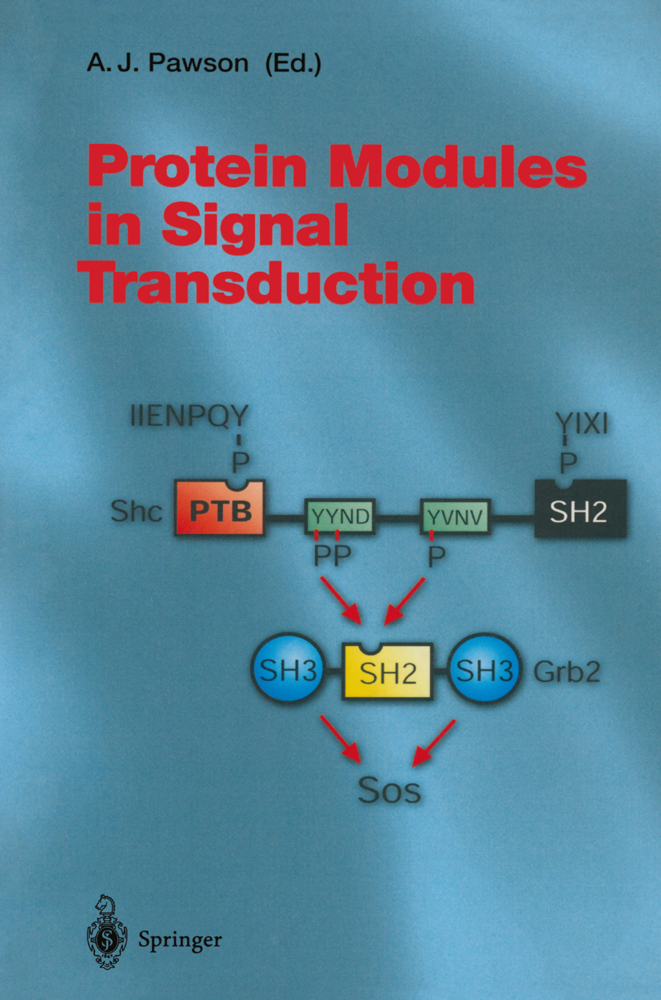
The behavior of eukaryotic cells, particularly those of multicel lular organisms, depends on the transmission of signals from one cell to another. Such extracellular signals can take the form of hormones, antigens, cells surface molecules, or components of the extracellular matrix and exert their effects by binding to specific receptors, usually exposed on the surface of the target cell. These transmembrane receptors possess a cytoplasmic domain that al lows communication with intracellular signaling pathways, pro viding access to the regulation of gene expression, cytoskeletal architecture, cell metabolism, survival, and the cell cycle. Defining the process through which a signal emanating from an individual receptor can influence so many aspects of cellular function is of central importance for our understanding of signal transduction. Many polypeptide factors that regulate cellular growth and differentiation bind to receptors with cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domains. Recent evidence has indicated that intracellular sig naling from receptor tyrosine kinases proceeds through a series of modular protein-protein interactions, typified by the interaction of autophosphorylated growth factor receptors with the Src ho mology 2 (SH2) domains of cytoplasmic target proteins. Thus, a crucial role of tyrosine phosphorylation is to promote the for mation of protein complexes through the creation of specific SH2 domain-binding sites, thereby regulating the activation of bio chemical pathways within the cell.
Function of PTB Domains
Pleckstrin Homology Domains
Structure and Function of LIM Domains
WW (WWP) Domains: From Structure to Function
Modular Domains of Focal Adhesion-Associated Proteins
Physiological Function of Receptor-SH2 Interactions
The IRS-Signaling System: A Network of Docking Proteins That Mediate Insulin and Cytokine Action
PDZ Domains and the Formation of Protein Networks at the Plasma Membrane
Mechanism and Function of Signaling by the TGFß Superfamily
Notch Receptors, Partners and Regulators: From Conserved Domains to Powerful Functions
Signaling Through Grb2/Ash-Control of the Ras Pathway and Cytoskeleton
Genetic Analysis of Sevenless Tyrosine Kinase Signaling in Drosophila.
List of Contents
Functions of SH2 and SH3 DomainsFunction of PTB Domains
Pleckstrin Homology Domains
Structure and Function of LIM Domains
WW (WWP) Domains: From Structure to Function
Modular Domains of Focal Adhesion-Associated Proteins
Physiological Function of Receptor-SH2 Interactions
The IRS-Signaling System: A Network of Docking Proteins That Mediate Insulin and Cytokine Action
PDZ Domains and the Formation of Protein Networks at the Plasma Membrane
Mechanism and Function of Signaling by the TGFß Superfamily
Notch Receptors, Partners and Regulators: From Conserved Domains to Powerful Functions
Signaling Through Grb2/Ash-Control of the Ras Pathway and Cytoskeleton
Genetic Analysis of Sevenless Tyrosine Kinase Signaling in Drosophila.
Pawson, Anthony J.
| ISBN | 978-3-642-80483-0 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783642804830 |
| Medientyp | Buch |
| Auflage | Softcover reprint of the original 1st ed. 1998 |
| Copyrightjahr | 2011 |
| Verlag | Springer, Berlin |
| Umfang | IX, 368 Seiten |
| Abbildungen | IX, 368 p. |
| Sprache | Englisch |