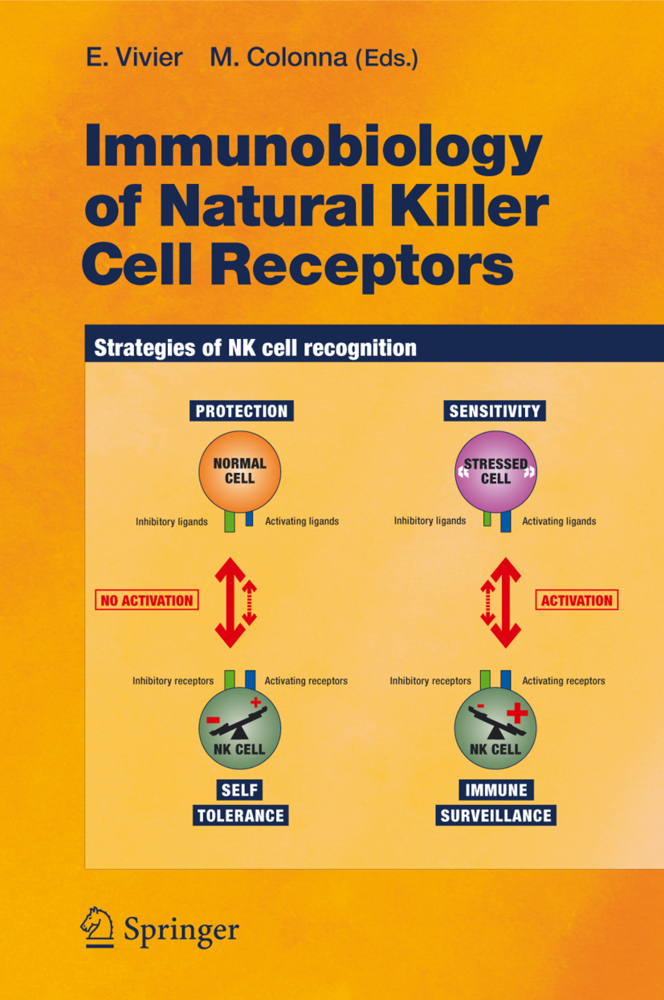
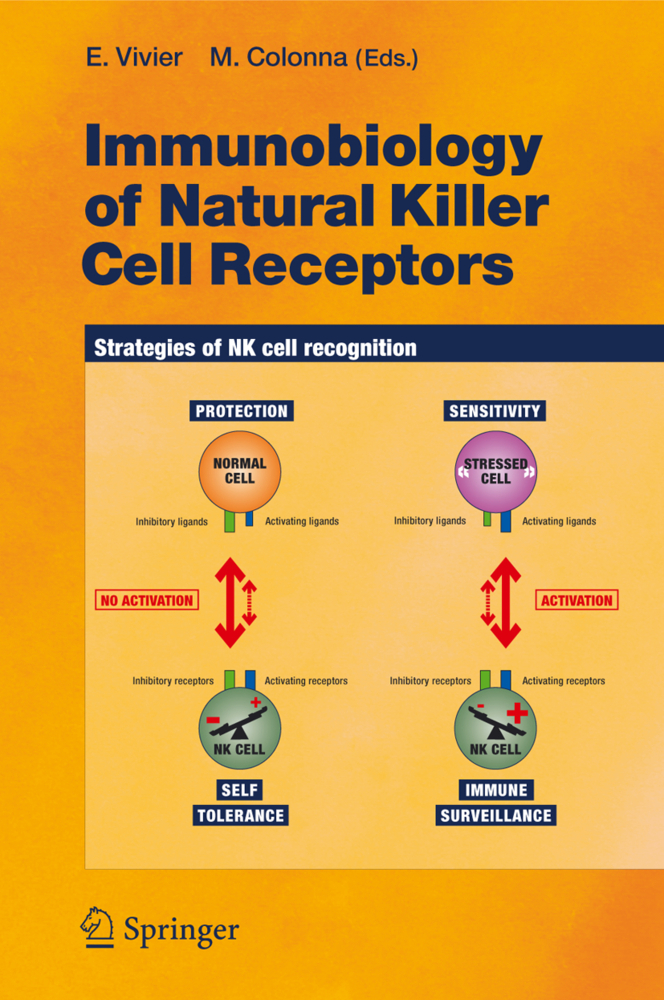
The immune system is not bound by a single tissue but is instead bestowed with the challenge of warding off invading pathogens throughout the body. Constant surveillance of the body requires that the immune system be highly mobile and able to purge pathogens from all tissues. Because each tissue presents its own unique architecture and milieu, it is necessary for the immune system to be as malleable as it is dynamic. For example, how the immune system handles a pathogen in the lung can differ significantly from a pathogen encountered in the gut.
1;Preface;62;Contents;83;Contributors;104;Two-Photon Imaging of the Immune System: A Custom Technology Platform for High-Speed, Multicolor Tissue Imaging of Immune Responses;144.1;1 Introduction;154.2;2 Description of Custom Two-Photon Instrumentation;244.3;3 Representative Data;344.4;4 Future Perspectives;364.5;References;395;Visualizing Intermolecular Interactions in T Cells;435.1;1 Introduction;445.2;2 Molecular Recruitment to the Immunological Synapse;455.3;3 Molecular Interactions in the Immunological Synapse;495.4;4 Variability in the Form of the T Cell:APC Interface;535.5;5 Concluding Remarks;555.6;References;556;Multiscale Analysis of T Cell Activation: Correlating In Vitro and In Vivo analysis of the Immunological Synapse;596.1;1 Introduction;606.2;2 Parameters in T Cell Activation;616.3;3 Immunological Synapses;666.4;4 Coordination of Antigen Recognition and Migration;716.5;5 Conclusions;766.6;References;777;T Cell Migration Dynamics Within Lymph Nodes During Steady State: An Overview of Extracellular and Intracellular Factors Influencing the Basal Intranodal T Cell Motility;837.1;1 Introduction;857.2;2 Extracellular Factors Influencing the Intranodal Migration Behavior of T Lymphocytes;887.3;3 Intracellular Factors Contributing to Intranodal T Cell Motility;1017.4;4 Computational Simulation of T Cell Migration and Interaction Dynamics: The In Silico Lymph Node Model;1067.5;5 Conclusion;1107.6;References;1128;Chemoattractant Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Lymphocyte Motility and Trafficking;1188.1;1 Introduction;1198.2;2 Major Chemoattractant Receptors that Function in Lymph Node Homing, Motility, and Egress;1198.3;3 Major Mediators of Chemoattractant Receptor Signaling;1218.4;4 Imaging Lymphocyte Trafficking and Motility;1248.5;5 Conclusions;1348.6;References;1359;New Insights Into Leukocyte Recruitment by Intravital Microscopy;1399.1;1 Introduction;1409.2;2 Advantages and Disadvantages of IVM;1419.3;3 Capturing;1429.4;4 Rolling;1459.5;5 Arrest;1479.6;6 Postadhesion Events;1499.7;7 Transmigration;1509.8;8 Organ Specific Recruitment;1529.9;9 Perspectives;1539.10;References;15410;Visualizing the Molecular and Cellular Events Underlying the Initiation of B-Cell Activation;16310.1;1 Introduction;16410.2;2 Tools for Visualizing B Cell Activation Events;16510.3;3 Visualizing Molecular Events During the Initiation of B Cell Activation;16810.4;4 Visualizing Intercellular Events During the Initiation of B Cell Activation In Vivo;17410.5;5 Conclusions;18110.6;References;18211;Tracking the Dynamics of Salmonella Specific T Cell Responses;18811.1;1 Introduction;18911.2;2 Studying Immunity to Salmonella;18911.3;3 Visualizing Salmonella In Vivo;19111.4;4 Adaptive Immunity in the Murine Typhoid Model;19111.5;5 Tracking Antigen-Specific Responses in Salmonella Infection;19311.6;6 Development and Function of Th1 Cells During Salmonella Infection;19911.7;7 Conclusion;20111.8;References;20112;Imaging Listeria monocytogenes Infection In Vivo;20812.1;1 Introduction;20912.2;2 Listeria Infection in Mice as a Model of Host Pathogen Interactions;21012.3;3 Innate Immune Responses to Listeria;21012.4;4 Adaptive Immunity to Listeria;21112.5;5 In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging Studies of Listeria Infection;21212.6;6 In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging Techniques;21412.7;7 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy;21712.8;8 Application of CLSM in Studying Listeria Pathogenesis;21812.9;9 Introduction to Two-Photon Microscopy;21812.10;10 2P Microscope Design;22012.11;11 Live Tissue Imaging and In Vivo Cell Dynamics;22212.12;12 2P Imaging Data Analysis;22312.13;13 2P Microscopy of Listeria Infection;22412.14;14 Using 2P Microscopy to Assess the Presentation of Bacterial Antigen In Situ;22512.15;15 Single-Cell Tracking of MZ Macrophages and PALS DCs;22612.16;16 2P Microscopy can Detect Individual Bacteria in Infected Host Cells;22712.17;17 Future Directions;22912.18;References;229
McGavern, Dorian
Dustin, Michael
| ISBN | 9783540938644 |
|---|---|
| Artikelnummer | 9783540938644 |
| Medientyp | E-Book - PDF |
| Auflage | 2. Aufl. |
| Copyrightjahr | 2009 |
| Verlag | Springer-Verlag |
| Umfang | 292 Seiten |
| Sprache | Englisch |
| Kopierschutz | Digitales Wasserzeichen |